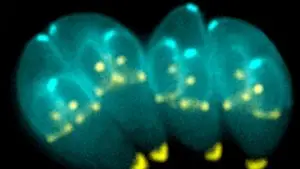
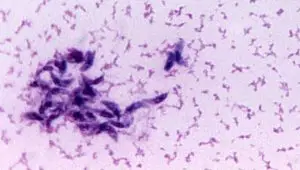
Toxoplasma Gondii
Understanding, recognizing, diverting
Dear reader,
In this specialist article we deal with the microparasite Toxoplasma Gondii in a well-known scientific, evidence-based and holistic manner.
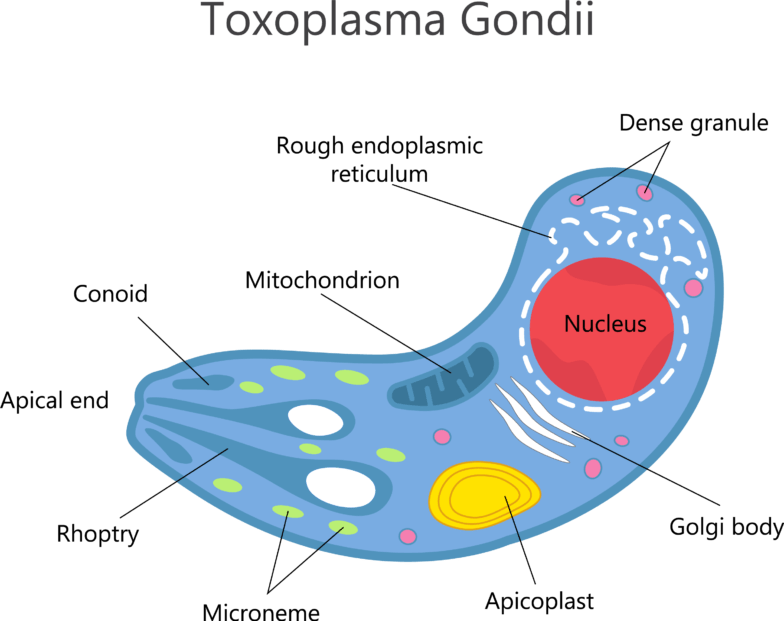
Toxoplasma Gondii – fact check:
- According to statistics from the Robert Koch Institute, 60% of the German-speaking population are infected with Toxoplasma Gondii [1].
- The parasite can attack the brain and trigger behavioral changes there [2].
- Toxoplasma Gondii can cause diseases such as toxoplasmosis , depression , schizophrenia or psychosis [3].
- Researchers like Prof. Dr. Jaroslav Flegr associate the brain parasite with character traits such as envy , distrust or introversion [4].
- Studies show that an infestation with the protozoa can lead to an increase in the cortisol level, which can trigger inner restlessness , nervousness and chronic stress can [5].
- A current study by TU Dortmund has shown that the memory performance of people infected with Toxoplasma Gondii can decrease by up to 30% [6].
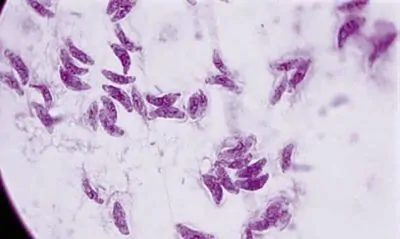
In this article we clarify the following questions:
- Is there a reliable test to diagnose Toxoplasma Gondii?
- How does transmission to humans take place?
- Which symptoms can occur in the event of an infestation with Toxoplasma Gondii?
- What does a behavior change induced by the parasite look like?
- Toxoplasma Gondii in pregnancy - dangerous or harmless?
- What options for treatment are available?
Toxoplasma Gondii – pulling the cord in the human brain –
An exclusive information video from the Swiss Parasite Free Association –
Look at you here the entire Parasite Academy free of charge.
The Test
The non-profit Swiss association Parasitenfrei has had a free online test developed by doctors in collaboration with programmers. This allows an expert assessment to be obtained from home as to whether there is an active infection with Toxoplasma Gondii.

- The parasite test by the Swiss Parasite Free Association
Laboratory diagnostics can also be used to attempt to detect the microparasite. Antibody detection is usually collected for this. [7] However, this test is quite error-prone , since the antibodies IgG and IgM can also occur physiologically increased or decreased in the serum and the results therefore often are not significant [8]. The costs for the Toxoplasma Gondii test are between 15 and 25 euros . The collection of venous blood by a doctor is necessary [9].
Behavior change
It has only been known for a few years that the microparasite Toxoplasma Gondii is not only relevant for pregnant women, but for all people , as it is able to significantly change behavior [10].
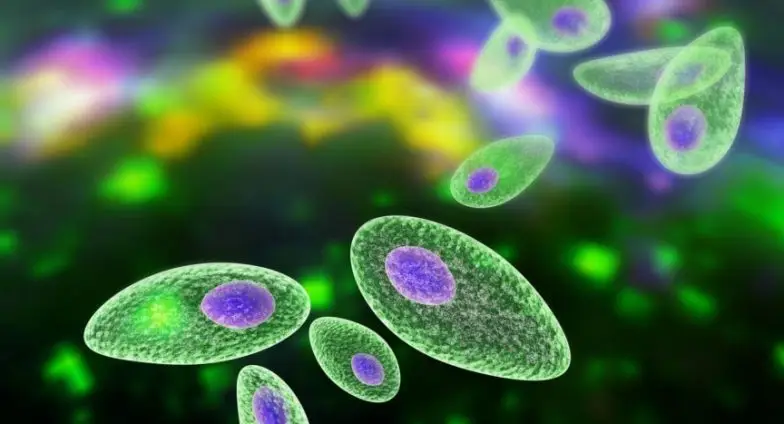
How does he do that?
Human behavior is crucially dependent on the hormone cocktail in the blood [11]. The endocrinologist Martin Wabitsch from the Ulm University Hospital says about it [12]:
The amount of cortisol released under stress determines, for example, whether someone acts fearfully or brave [14] . Peptide hormones can make trustworthy and malicious at the same time [15] . A dopamine deficiency can mean that our feeling of happiness is not pronounced. And without dopamine there would be neither crime nor obesity [16].
Today we know that Toxoplasma Gondii has massive effects on the hormonal system [17] and thereby also affects our behavior.

Parasites in the brain: why 60% of people are affected –
An exclusive information video from the Swiss Parasite Free Association –
Look at you here the entire Parasite Academy free of charge.
Important Information
Toxoplasma Gondii can occur in humans in active and inactive form. Only when activated does it have an influence on behavior . It is possible that the parasite [18]:
- Is already active shortly after infection
- Activated ad hoc at any time
- Changes from the active to the inactive state at any time
What exactly does this change in behavior look like?
An active infestation can therefore be accompanied by a change in behavior by influencing hormones. This parasitic changed behavior can [19]:
- Already exist since birth (transmission in the womb)
- Show yourself suddenly (activation of the parasite in the event of an infection or contagion and immediate activation)
- Changeable (activation / deactivation alternately within a certain period of time)

Whether and which changes in behavior occur in an infected person, varies greatly. For example, some people become more introverted and others more willing to take risks [20]. It has not yet been clarified whether it is pure coincidence which behavioral changes are induced or whether there is a logic behind it.
Possible behavior patterns under the influence of Toxoplasma Gondii are [21]:
- Change of character ( "I don't recognize you anymore" )
- Increased willingness to take risks
- infidelity
- Mood swings, Bad mood
- irritability, Anger, aggression
- anxiety
- lethargy, Introversion
- irresponsibility
- mistrust
- envy
- slowness, extended response time ("difficult to understand")
Attention!
A change in behavior is only one possible symptom among many. If there is no different behavior, other symptoms can still appear. More on this in our paragraph „Toxoplasma Gondii – the symptoms“.
Transmission to humans
The following routes of transmission from Toxoplasma Gondii to humans are known:
1. About gardening

The T.G. lives in a certain stage of development (sporulated oocysts) in the soil . It gets there via older feces from cats or mice, for example, and lasts up to 5 years . Oral ingestion of the smallest amounts of contaminated soil is sufficient for transmission [22].
Note
An infection with Toxoplasma Gondii (regardless of the source) is usually silent [23], that is, without the appearance of direct symptoms . An infection often only shows up years later , for example in a change in behavior or depression [24].
2. About ingestion of contaminated meat

By eating the meat of infected animals , the Toxoplasma Gondii can be transmitted to humans. Freezing (at least -21 ° C) or heating (at least 50 ° C core temperature) for at least 20 minutes kills the pathogen [25].
3. Via tap water

If the pathogen is in the earth, it is inevitable that it will also find its way into the groundwater [26]. Single-cell microbes are not killed across the board by the waterworks [27]. This is how the contaminated drinking water gets into households.
Note
According to the Drinking Water Ordinance, tap water is not (!) Tested for microbes [28]. Therefore, there is no data on the regions in which drinking water is contaminated with Toxoplasma Gondii. The fact is that tap water basically contains parasites. More information and proof of this here can be obtained.
4. Transplacental transmission in the womb
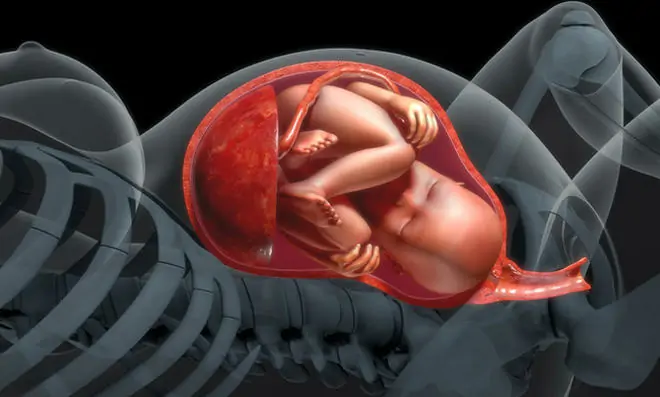
If the mother is infected with Toxoplasma, the pathogen can be transmitted in utero to the child [29]. Mental illnesses in children, e.g. “ADHD”, can be caused by an infection with Toxoplasma Gondii [30].
5. Through contact with cats or cat poop

Mice become infected with the single-celled parasite through contaminated soil. A journey from the mouse to the human brain now begins for the Toxoplasma Gondii [31]:
Note
Dr. Jaroslaw Flegr points out that, as a result of his research, all people who have had closer contact with cats in their life are infected with Toxoplasma Gondii [32].
The life cycle (life cycle) [33]
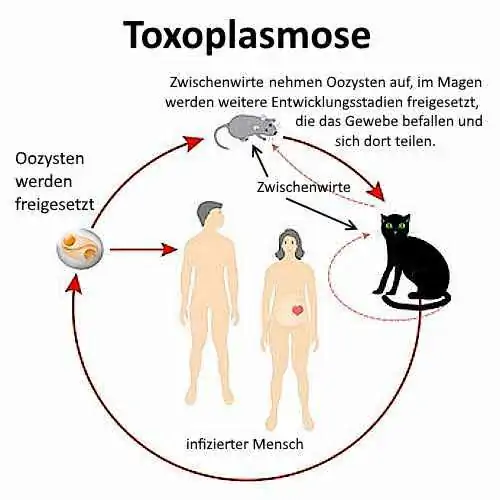
The single-celled parasite penetrates the brain of the mouse and changes there the behavior of the rodent significantly. By forming cysts it lowers the perception of risk . In addition, the parasite influences the dopamine balance in the mouse, causing it to lose its innate fear of cats . Changes in the olfactory cranial nerve also make the mouse feel attracted to cat urine.

What must happen happens: The mouse is eaten by the cat and thus it is infected with Toxoplasma Gondii . After all, humans become infected through contact with cats or their excretions.
Once in the human bloodstream, the parasite takes over an immune cell and steers it in the direction of the brain. The blood-brain barrier lets the immune cell pass and the parasite has managed to get into the human brain unhindered. It spreads in the neocortex (“control unit” of humans) and from this position has the most diverse possibilities of manipulation .
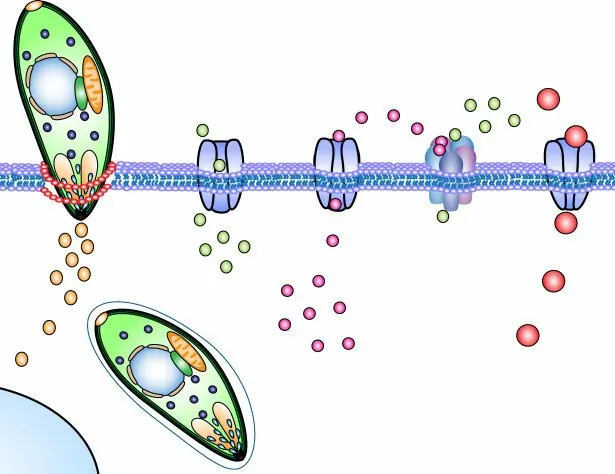
The molecular biologist Prof. Antonio Barragan has made the process how the Toxoplasma Gondii uses an immune cell to get into the human brain visible with the help of state-of-the-art technology:
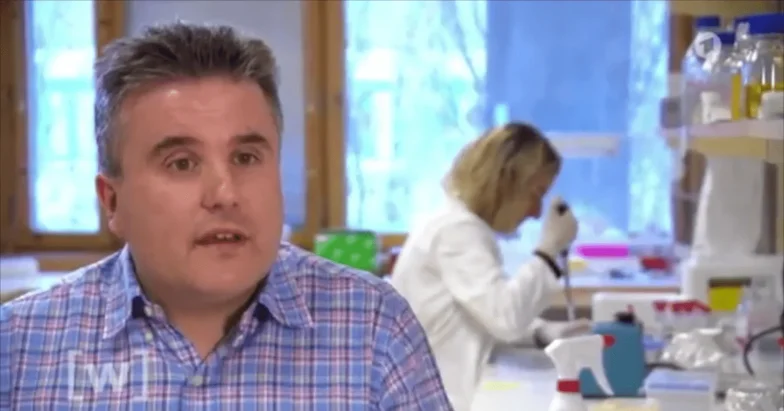

Information
The blood-brain barrier protects the brain from pathogenic agents such as parasites. They can not pass the barrier. Until 2012 it was completely unclear how the Toxoplasma Gondii managed to overcome the barrier in order to penetrate the host’s brain for manipulation purposes. A research group from the Francis Crick Institute, London, was the first research group worldwide to visualize the path of the parasite into the brain using imaging methods. The microparasites take over immune cells in order to hide from the blood-brain barrier. You practically use one „Trojanisches Pferd“ [35].
The treatment
We recommend a holistic treatment for Toxoplasma Gondii Parasitenkur.
Note
When choosing the cure, it must be ensured that the program includes the removal of the single-celled parasite .
The use of individual remedies (such as Syrian rue or colloidal silver) was unsuccessful according to our studies. After 6 weeks of use, none of our test subjects were free from brain parasites.
The success rate of a parasite cure designed for brain parasites, on the other hand, was 94% .
We have summarized further information on this in our large Parasite Cure Guide .
In our experience, drugs are ineffective because the toxoplasma in cysts in the brain protects itself from drugs [36].
Instead, a suitable parasite cure helps the body to enable itself to expel the Toxoplasma Gondii . As with Toni:

Attention!
Drug therapy is usually administered for 6 – 12 months . During this time it is not uncommon for permanent side effects to occur [38], how:
- fatigue
- sleep disorders
- fever
- Gastrointestinal complaints
- diarrhea
- Flatulence
- nausea
- Skin irritation
- Inflammation on and in the body

In rare cases, the following side effects can also occur [39]:
- Liver damage
- Disturbances in biliary activity
- Intestinal inflammation
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Allergic reaction
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Mycosis (fungal infection of the body)
The symptoms
As a rule, an infection is not noticeable at first. An active Toxoplasma Gondii will produce unspecific symptoms , such as [40]:
- Behavioral problems
More about this in ourParagraph “Changes in behaviorin this article. - Mood swings
- Listlessness
- Depressed mood, dejection
- Inner unrest
- Feeling of dissatisfaction
- nervousness
- Aggression / irritability
- Anxiety / panic attacks
- Fog in the head / feeling like "wrapped in cotton wool"
- lethargy
- Numbness / lack of emotion
- Bad memory
- Low attention span
- Low sex drive / increased sex drive
- Not to feel like "master of himself" / feeling of External control
Parasites: Mind Control in Humans –
An exclusive information video from the Swiss Parasite Free Association –
Look at you here the entire Parasite Academy free of charge.

Toxoplasma Gondii diseases:
The brain parasite can trigger other diseases in addition to toxoplasmosis, such as [41]:
- schizophrenia
- depressions
- Bipolar Disorder / Manic Depression
- Psychose
- ADS / ADHS
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Burnout syndrome
- eating disorder
- Personality disorders
- Addictions
Depression: Parasites Unnoticed Triggers –
An exclusive information video from the Swiss Parasite Free Association –
Look at you here the entire Parasite Academy free of charge.

Danger in pregnancy
If the Toxoplasma Gondii causes toxoplasmosis during pregnancy , this can be dangerous for the unborn child. Toxoplasmosis can be the T.G. effect only within six weeks after infection [42].
Therefore, you should pay attention to the following within a period of at least 6 weeks before the pregnancy [43]:
- Do not consume raw meat (especially no pork, game, lamb and goat)
- Avoid contact with cats or their shedding
- Refrain from gardening
- Do not drink tap water
Further information on the transmission of Toxoplasma Gondii to humans can be found here can be read.

Note
Toxoplasmosis is usually symptom-free . An infection is not noticed . There is only a direct danger to the child in the first 6 weeks after infection with Toxoplasma Gondii. Nevertheless, we recommend the elimination of the parasite before the beginning of the pregnancy, as it can pass to the unborn child. Already 60% of the German-speaking population is infected with the Toxoplasma parasite. It is therefore obvious that the mother-to-be is the carrier of Toxoplasma Gondii, especially if the woman with her is the one listed here Symptoms of an infestation notices. The means of choice for deriving the T.G. is a Parasitenkur.
Possible complications in pregnancy
A fresh Toxoplasma infection can cause serious complications and deformities of the fetus during pregnancy, such as [44]:
- Miscarriage
- Inflammation of the baby's eyes
- Hydrocephalus ("head of water")
- Calcification of the baby's cerebral vessels
- Prenatal damage to the liver and spleen
The Toxoplasma Gondii FAQ: Short question, short answer
The questions about Toxoplasma Gondii are answered by our association member and Toxoplasma expert Waldemar Masur.
The Toxoplasma gondii differs both in the shape and in the size depending on the stage. The cells of infectious form are arcuate and reach sizes of two to five micrometers . The oocysts measure up to 11 micrometers , the tissue cysts up to 300 micrometers. Two different populations of sporozoites form, the tachyzoites and bradyzoites. There is no structural difference between these two forms.
Yes. Modern imaging methods make it possible to make the microparasite visible. Here you can see two pictures:
Absolutely. I am pleased that this topic is also present in the leading media and that more people are realizing that a Parasitenkur represents the most important health decision in the 21st century.
For the most part already. However, we have put great hope in his statement that the T.G. with a Syrian rue and “joy meditation”. In our studies, this did not work.
Yes, the dog plays a role as a zoonosis . The animal can eat contaminated cat feces and become infected with it. After an infection, a dog doesn’t get any symptoms , but excretes the oocyst with the feces. Humans can become infected orally. Rolling around in cat feces can also contaminate the dog’s coat with oocysts. After 2-4 days in the environment, the oocysts become infectious and can infect humans or other warm-blooded animals perorally.